| em := TMenuItem.Create;
AboutItem := TMenuItem.Create;
MainMenu.MenuItems.Add(FileItem);
MainMenu.MenuItems.Add(HelpItem);
FileItem.MenuItems.Add(ExitItem);
FileItem.Text := ''''File'''';
ExitItem.Text := ''''Exit'''';
ExitItem.add_Click(ExitItemClick);
HelpItem.MenuItems.Add(AboutItem);
HelpItem.Text := ''''Help'''';
AboutItem.Text := ''''About...'''';
AboutItem.add_Click(AboutItemClick);
DoitButton := TButton.Create;
with DoitButton do
begin
Left := 8;
Top := 8;
Width := 33;
Height := 25;
Text := ''''Go'''';
add_Click(DoitButtonClick);
end;
CelsiusEdit := TSpinEdit.Create;
with CelsiusEdit do
begin
Left := 48;
Top := 8;
Width := 177;
Value := FloatToDecimal(100);
Maximum := FloatToDecimal(10000);
Minimum := FloatToDecimal(-1000);
add_ValueChanged(DoitButtonClick);
end;
ResultList := TListBox.Create;
with ResultList do
begin
Left := 8;
Top := 40;
Width := 217;
Height := 217;
end;
ClientSize := System.Drawing.Size.Create(240, 270);
Menu := MainMenu;
Controls.Add(DoitButton);
Controls.Add(CelsiusEdit);
Controls.Add(ResultList);
Text := ''''ConvertIt!'''';
ControlBox := True;
MinimizeBox := True;
Convert;
end;
begin
Form1 := TForm1.Create;
TApplication.Run(Form1);
end.
Note! The unit Borland.Delphi.Conversions contains the various Celsius temperature conversion routines. The unit Borland.VCL.Controls is a preliminary version that will not be included with the initial preview release.
The source code listed above is contained in ConvertIt.dpr, and is sure to change even before we ship the .NET preview compiler with Delphi 7. If we compile it, we''''ll see:
[d:d4.netconvert.net]dccil ConvertIt.dpr
Borland Delphi Version 16.0
Copyright (c) 1983,2002 Borland Software Corporation
Confidential pre-release version built Aug 2 2002 17:29:33
Borland.Delphi.Conversions.pas(60)
Borland.Vcl.Controls.pas(38)
ConvertIt.dpr(159)
260 lines, 0.64 seconds, 12232 bytes code, 0 bytes data.
After compiling the application, of course we should run it. Here''''s what the application looks like after a little resizing to minimize the image size. 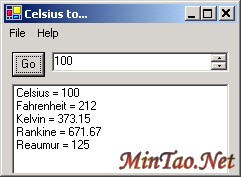
Fully Managed Code
This application is a 100% managed code application, as the results of PEVerify show:
[d:d4.netconvert.net]peverify ConvertIt.exe
Microsoft (R) .NET Framework PE Verifier Version 1.0.3705.0
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation 1998-2001. All rights reserved.
All Classes and Methods in ConvertIt.exe Verified
You can use Microsoft IL Disassembler (ildasm) to examine the executable.
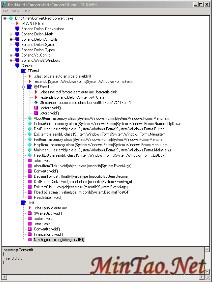
ILDasm running on ConvertIt.exe
You can examine the .NET assembler code for any module.
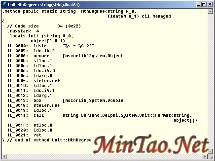
.NET assembler code for function NthDegree
Delphi for .NET code also works with Lutz Roeder''''s excellent utility, Reflector. (This link contains some other great .NET utilities as well.)
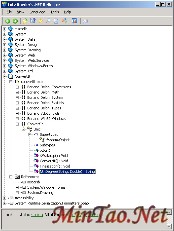
ConvertIt examined in Reflector
The .NET compiler
The Delphi for .NET compiler is more than just a port of the existing Delphi compiler. There is a new code generator, a new linker, significant new syntax, and a new runtime library. Of course, it is also very important to maintain language compatibility, so you will see some familiar old friends in Delphi for .NET as well:
- Strings & Arrays
- Records
- Classes
- Interfaces
- Properties & Events
- Sets
- Text files
- Local Procedures
- Variants
- Components
- Streams
- New, Dispose
- Readln, Writeln
- Format
- Component Streaming
- Random
In order to fully embrace the CLR and make Delphi a first class citizen in the new world of managed code, some language features must be deprecated, and others are the subject of ongoing research. Though many of these details are still being researched and implemented, it is hoped that the following information will be useful for understanding the new language features of Delphi for .NET.
Unsafe code warnings in Delphi
Starting with Delphi 7, the compiler includes three new warnings that can help you locate code that is non-portable (i.e. it uses a deprecated language feature or type), or unsafe in the .NET Framework. In the .NET Framework, "unsafe" simply means that the code cannot be verified by the static analysis performed by the CLR when the code is loaded. The compiler can warn about the usage of unsafe types, unsafe code, and unsafe casts.
Unsafe types
PChar, PWideChar, and PAnsiChar
Untyped pointers
Untyped var and out parameters
File of <type>
Real48
Variant records (records containing overlapping fields)
Unsafe code
Absolute variables
Addr(), Ptr(), Hi(), Lo(), Swap() standard procedures
BlockRead(), and BlockWrite()
Fail()
GetMem(), FreeMem(), ReallocMem()
inline assembler
the @ operator
Unsafe casts
Casting an object instance to a type that is not an ancestor or descendent of the instance type
Casting a record type to anything else
These new warnings are disabled by default. They can be enabled with the IDE Project Options dialog box, or with the compiler directive:
{$WARN UNSAFE_CODE ON}
They can also be enabled with the -W command line switch:
dcc32 -W+UNSAFE_CODE
Note there is no space before or after the ''''+'''' character on the command line switch.
Note: These new warnings are in the Delphi 7 (and beyond) compiler for Win32 (dcc32). They are not in the Delphi for .NET Preview compiler (dccil).
Deprecated Language Features
The dccil compiler will also deprecate some existing language features, listed in the following table.
Keyword/Language Feature |
Notes |
Real48 six byte floating type
GetMem(), FreeMem(), and ReallocMem()
Use dynamic arrays, or rely on automatic dispose pattern implementation
BlockRead(), BlockWrite()
Absolute directive, Addr, and @
Pre-Delphi object syntax (type foo = object)
TVarData, Variant internals
Variant semantics will be supported but not as TVarData
File of <type>
This construct cannot be implemented because the Delphi compiler cannot know the size of <type> on the target platform (e.g. a handheld device). The JIT compiler for the specific platform determines the size of intrinsic types.
Untyped var and out parameters
Untyped const parameters are still supported
PChar
In a future release Delphi for .NET will support unsafe managed code (i.e. pointers). Unsafe, unmanaged pointers are not supported in the preview release.
automated and dispid directives
Inline assembly - asm statement
TInterfacedObject
AddRef, QueryInterface, and Release are deprecated. In the preview release TInterfacedObject is an alias for TObject.
Dynamic aggregation
Dynamic aggregation of interfaces is not supported by the CLR, because it cannot be statically verified. In Delphi for .NET, all interfaces must be declared on the type. Dynamic aggregation is provided by the implements keyword, as the following code illustrates.
program Project1;
type
i = interface
procedure Wombat;
end;
TA = class(TInterfacedObject, i)
procedure Wombat;
end;
TC = class(TInterfacedObject, i)
fa: TA;
property a: TA read fa implements i;
end;
{ TA }
procedure TA.Wombat;
begin
end;
begin
end.
ExitProc
CLR and Delphi
The new Delphi compiler will provide access to the .NET CLR (Common Language Run-time). Delphi developers will be instantly familiar with the CLR not just because it resembles the VCL so clo 上一页 [1] [2] [3] [4] 下一页 |






