|
Thursday, March 15, 2001
By Ish Singh
Introduction:
COM is sometimes referenced as Common Object Model but Microsoft officially calls it Component Object Model. Microsoft also developed DCOM as an extension of COM. DCOM was designed with distributed computing in perspective. CORBA stands for Common Object Request Broker Architecture and developed by Object Management Group (OMG). COM/DCOM and CORBA among others are object-oriented approaches for the use and development of software components. They are the competing architectures for application development in the client/server world. These architectures support distributed computing and provide support for interoperability and limited portability. Distributed computing technologies are necessary for creating flexible client/server systems. These distributed objects can exist anywhere on the system as they encapsulate the data and business logic within themselves. As heterogeneous systems are getting more and more popular, distributed objects are also getting popular, as they are really good at connecting these heterogeneous systems.
CORBA and DCOM are both designed for client/server style communication among distributed objects. In both technologies, a client invokes a method that is implemented by a remote object that acts as a server. The interface for such an object providing the service is defined in an Interface Definition Language (IDL). This keeps the object implementations hidden from the client. Both CORBA and COM communications are implemented like RPC and methods of remote objects are invoked on reference. The support for data types in both these technologies is limited to a few data types that can be mapped to multiple programming languages.
Origin:
Its predecessor OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) was originally used for linking documents on Microsoft Win 3.1 OS. COM was developed to integrate components dynamically within a single address space. COM was designed to provide support of dynamic use of multiple vendor binary components in one single application. Component interactions are based on OLE2 interfaces and protocols. Although COM uses OLE2 interfaces and protocols, it is worthy to know that COM is not OLE. DCOM was developed as an extension of COM to allow network based interactions and allows processes to be spread across a network.
Common Object Request Broker Architecture was developed by Object Management Group (OMG). OBG is a consortium of hundreds of companies that are working to the adapt a standard architecture for distributed object computing. CORBA is based on Object Management Architecture, which was published in 1991 by the OMG. CORBA was developed to provide vendors with a standard architecture that allows them to develop applications using different languages, operating systems, and hardware and still provide the portability and interoperability.
Technical View:
COM allows clients to invoke services provided by COM-compliant components by defining a binary compatibility specification and implementation. COM compliant components (COM Objects) provide a set of interfaces that allow a client to contact the Object using those interfaces only.
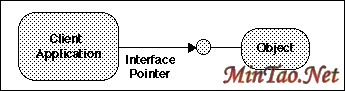
COM defines the binary structure between the client and the Objects and is the basis for interoperability between components written in multiple programming languages as long as the language compiler supports Microsoft抯 COM binary structure.
COM objects can have multiple interfaces but each class must have its own unique class ID (CLSID) and its interface must have Globally Unique Identifier (GUID) to avoid name collisions. Objects and interfaces are defined using Microsoft抯 IDL (Interface Definition Language). COM architecture does not allow for easy modification of the interfaces and their methods to help prevent potential version incompatibilities. COM developers are rather encouraged to build new interfaces to the objects to provide additional functionality. COM objects run inside of a server, and the server provides three ways for the clients to access COM Objects.
- In-process server: Client and Server run in the same memory process and communicate among each other using function calls.
- Local Object Proxy: This allows clients using an inter-process communication mechanism to access server running in a different process but on the same physical machine. This inter-process mechanism is also known as lightweight remote procedure call.
- Remote Proxy Object: This allows clients to access remote servers running on another machine. Clients and servers communicate using distributed computing environment RPC. Remote objects supporting this mechanism are called DCOM Servers.
Two major extensions to COM: MTS and MSMQ are provided by DCOM. DCOM Server Objects provide support for multiple threads. MTS (Microsoft Transaction Server) runs on Windows NT Server and provides transaction oriented processing and is based on the DTC (Distributed Transaction Coordinator). MTS is included in DCOM as a runtime middle-ware environment that provides asynchronous application operation with MSMQ and synchronous operation with RPC (Remote Procedure Call). DCOM also has remote garbage collection functionality built into it, which makes it a robust system.
CORBA is designed and structured to allow integration of multiple object systems written in different languages and running on different platforms. CORBA relies on ORB middle-ware for communication between the server and the client. ORB acts as an object that connects remote objects transparently. Each CORBA object exposes an interface that has a set of methods attached to it. ORB is responsible for finding the object implementation for the request and to format and communicate request to the CORBA server. ORB provides transparency to the client, and the client never needs to know about the location of the remote object and what language was used to implement it.
CORBA is based on Object Management Architecture (OMA), and OMA defines a broad range of services for building distributed applications. OMA services are divided into three layers named CORBAServices, CORBAFacilities, and ApplicationObjects. ORB communication infrastructure is required for applications to access these services. These services are actually definition of different categories of objects in OMA and define a broad range of functionality needed to support distributed applications.
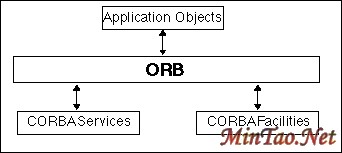
- CORBAServices: are the necessary building blocks for developing distributed applications. These services provide asynchronous event management, transactions, persistence, concurrency, naming, relationships, and lifecycle management.
- CORBAFacilities: are not necessary for developing distributed applications but can be useful in some cases. These facilities provide information management, system management, task management, and user interface.
- ApplicationObjects: are dedicated to providing service to a class of application or a specific application. These are either basic services, support common facilities or application-specific services.
CORBA interfaces and data types are defined using OMG Interface Definition Language. Each interface抯 methods are also defined using OBG IDL. IDL is the key part of CORBA architecture that provides mapping of data types between CORBA and programming languages. IDL also allows for easy encapsulation of legacy code. IDL is an object-oriented interface definition language with syntactic similarities with C++. As all the interfaces are defined in IDL, CORBA specifications allow for client and objects to be written in different languages while keeping the details transparent from each other. CORBA uses IIOP (Internet Inter-ORB Protocol) for communication among various object request brokers using TCP as the network transport.
CORBA components include ORB Core, ORB Interface, IDL Stub, DII (Dynamic Invocation Interface), Object Adaptor, IDL Skeletons, and DSI (Dynamic Skeleton Interface). CORBA runtime infrastructure (ORB Core): is vendor specific and is not defined by CORBA. However, ORB interface is a standard interface to functions provided by all CORBA compliant ORBs. IDL processor generates stubs for each interface. This hides the low-level communication and provides a high-level, object-type specific API. DII is an alternative to the IDL stubs that provides a generic mechanism for constructing requests at run-time. Object Adaptor, provides ability to integrate alternative object technologies into the OMA. IDL skeletons are similar to IDL stubs but they provide the server-side (object implementation). Object Adaptor sends requests to the IDL skeletons, which in turn call, the appropriate methods in the object implementation.
Technical Comparison:
CORBA Relies on IIOP for communication with remote objects while DCOM relies on Object Remote Procedure Call (ORPC) for the same purpose. CORBA architecture is based on Object Request Broker while DCOM uses COM as its basis and for transaction processing it relies on MTS or MSMQ. CORBA specification is not vendor specific and hence CORBA applications can run on multiple hardware platforms. On the other hand, DCOM is Microsoft抯 proprietary architecture and runs only on hardware supported by Microsoft operating systems. CORBA allows for multiple inheritance while DCOM only provides single inheritance. DCOM uses ping ev [1] [2] 下一页
[Web开发]VS2005+SQL2005之.NET2.0数据库连接 [Web开发]VS2008和.NET3.5Beta2新特性(介绍及下载地址)
[Web开发]通过VS2005如何发布网站 [Web开发]VS2005安装了SP1后发布项目存在的问题之解决方案
[Web开发]VS2005如何建立(新建)网站项目 [Web开发]图文解说—如何通过VS2005测试网站程序性能
[聊天工具]Google Suggest十大妙用 [聊天工具]保驾护航Web迅雷 全新版本给你更多安全
[聊天工具]玩转火狐的Cookie 让火狐狸吃好小甜饼! [聊天工具]P2P下载的好工具 POCO完全攻略
|